Using Coulomb Diamond Models
Installation
We recommend using pip, poetry, or uv to install the package.
Authentication
The SDK requires an API key for authentication. Sign in and create a new API key. Remember, your API key is your access secret—keep it safe with environment variables.
Using environment variables:
Or provide the API key directly:
Usage Examples
Using the Coulomb Diamond Segmenter
The Coulomb Diamond Segmenter is a binary segmentation model that segments a given conductance measurement grid into coulomb diamond regions.
You can download an example file to follow along with the example:
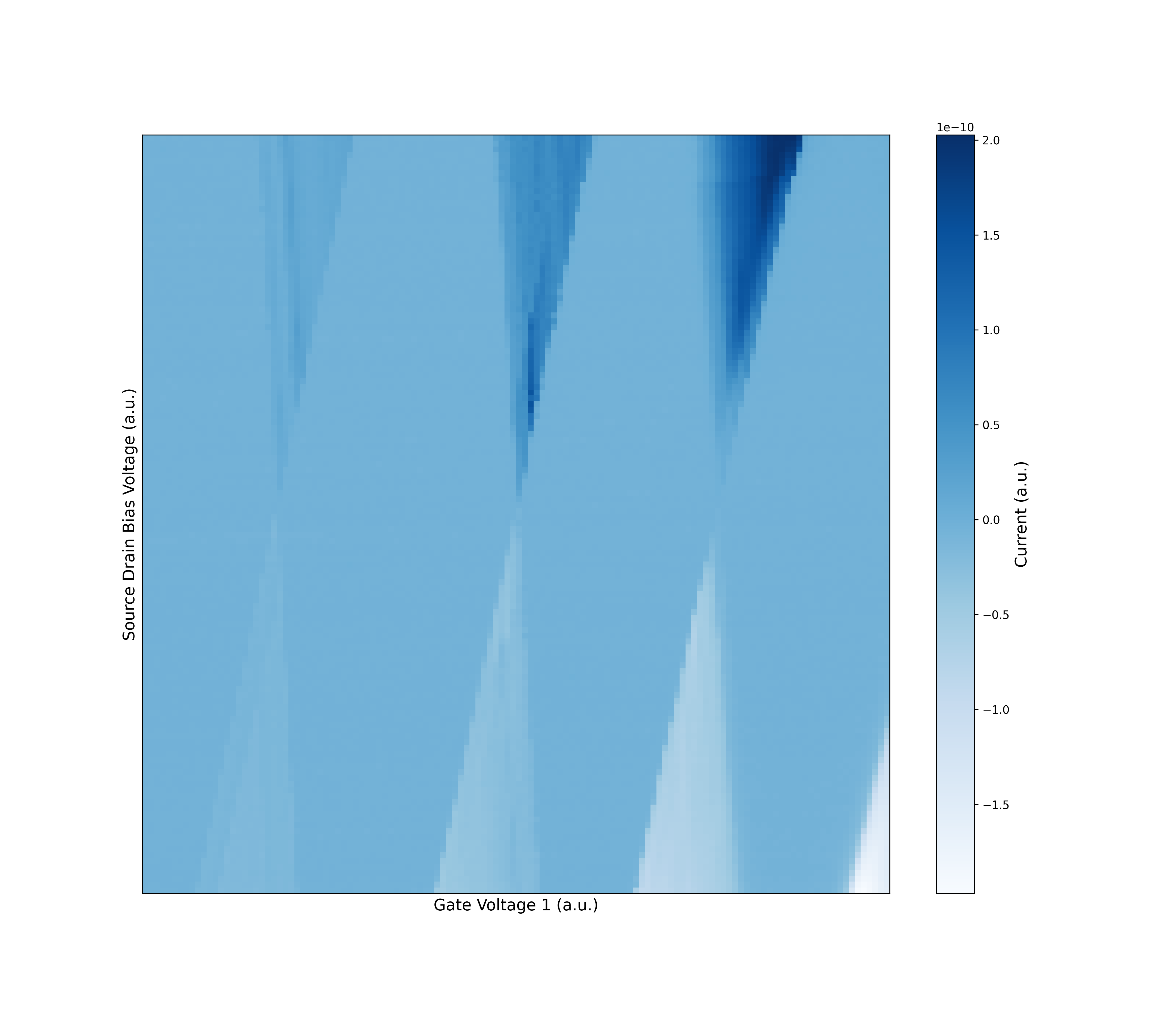
Coulomb Diamond Segmenter v0 Input Data. (Data Source: Lennon, D., et al. Real measurement of Coulomb diamonds. 2019. Zenodo, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2559478.)
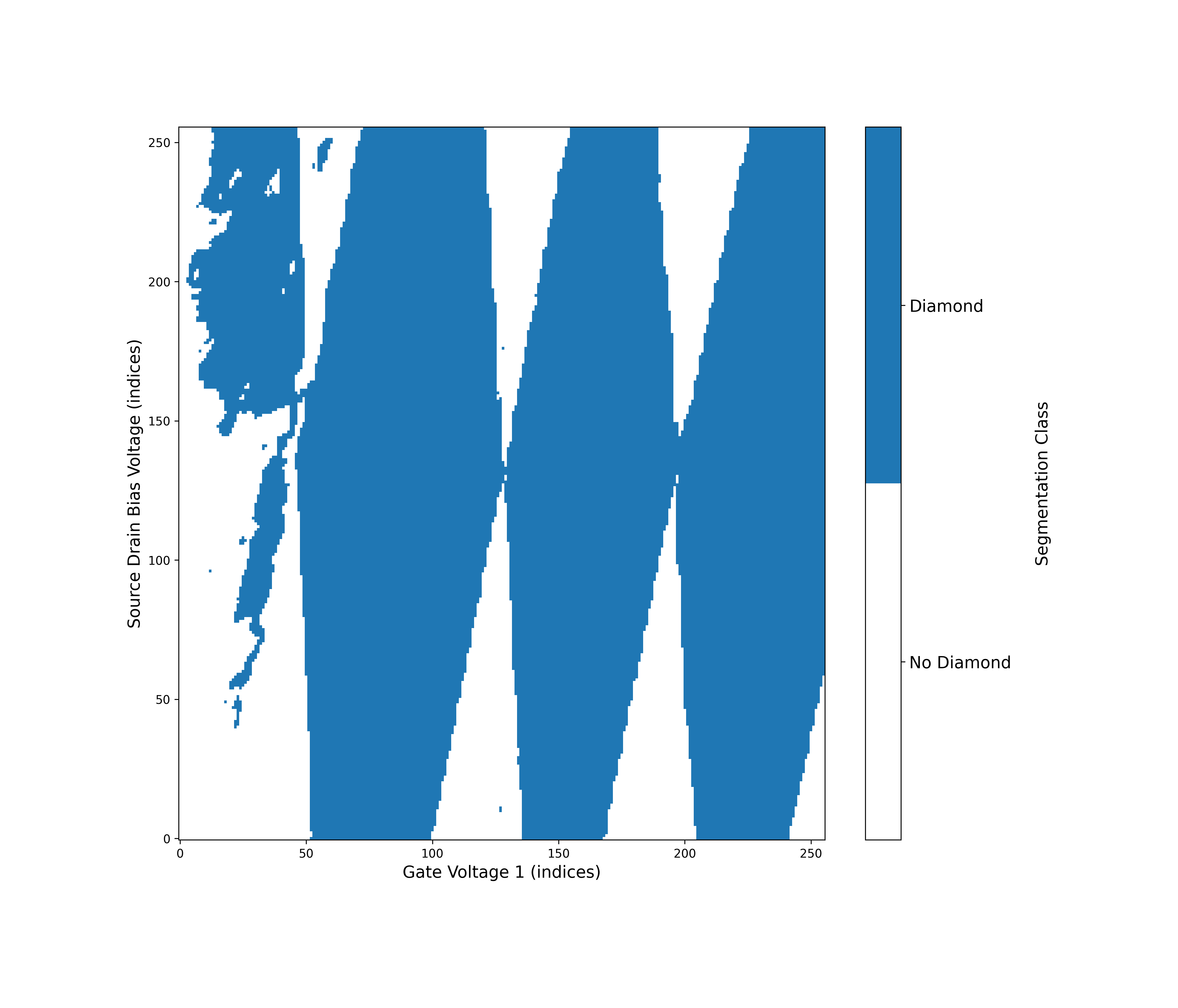
Using the Coulomb Diamond Detector
The Coulomb Diamond Detector is a model that detects Coulomb Diamond structures from a binary segmentation mask.
You can download an example file to follow along with the example:
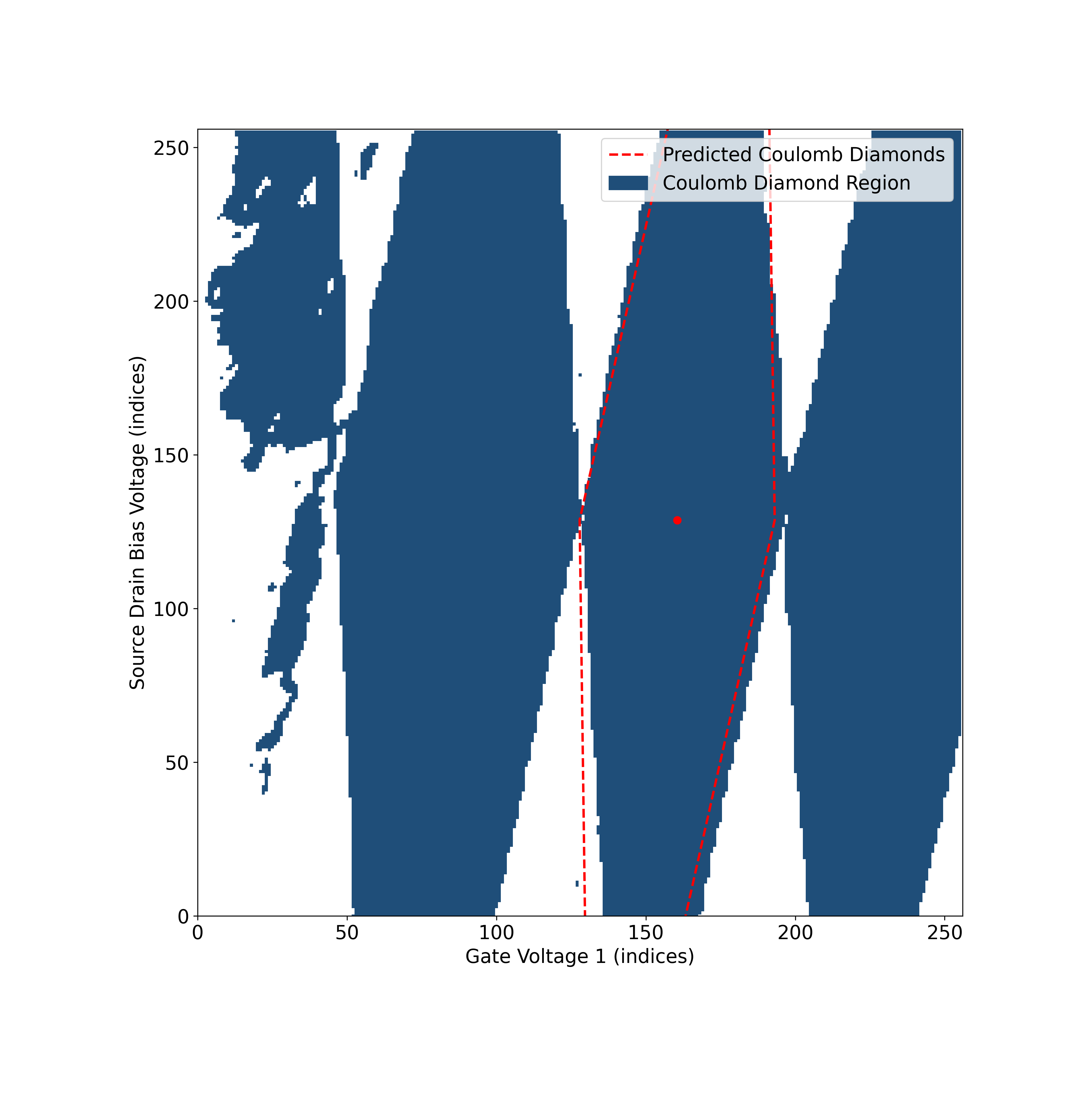
The four diamond keys “left”, “right”, “bottom” and “top” correspond to each vertex of the detected Coulomb diamond.
Plotting the Output
Use the following script to visualize detected coulomb diamonds.
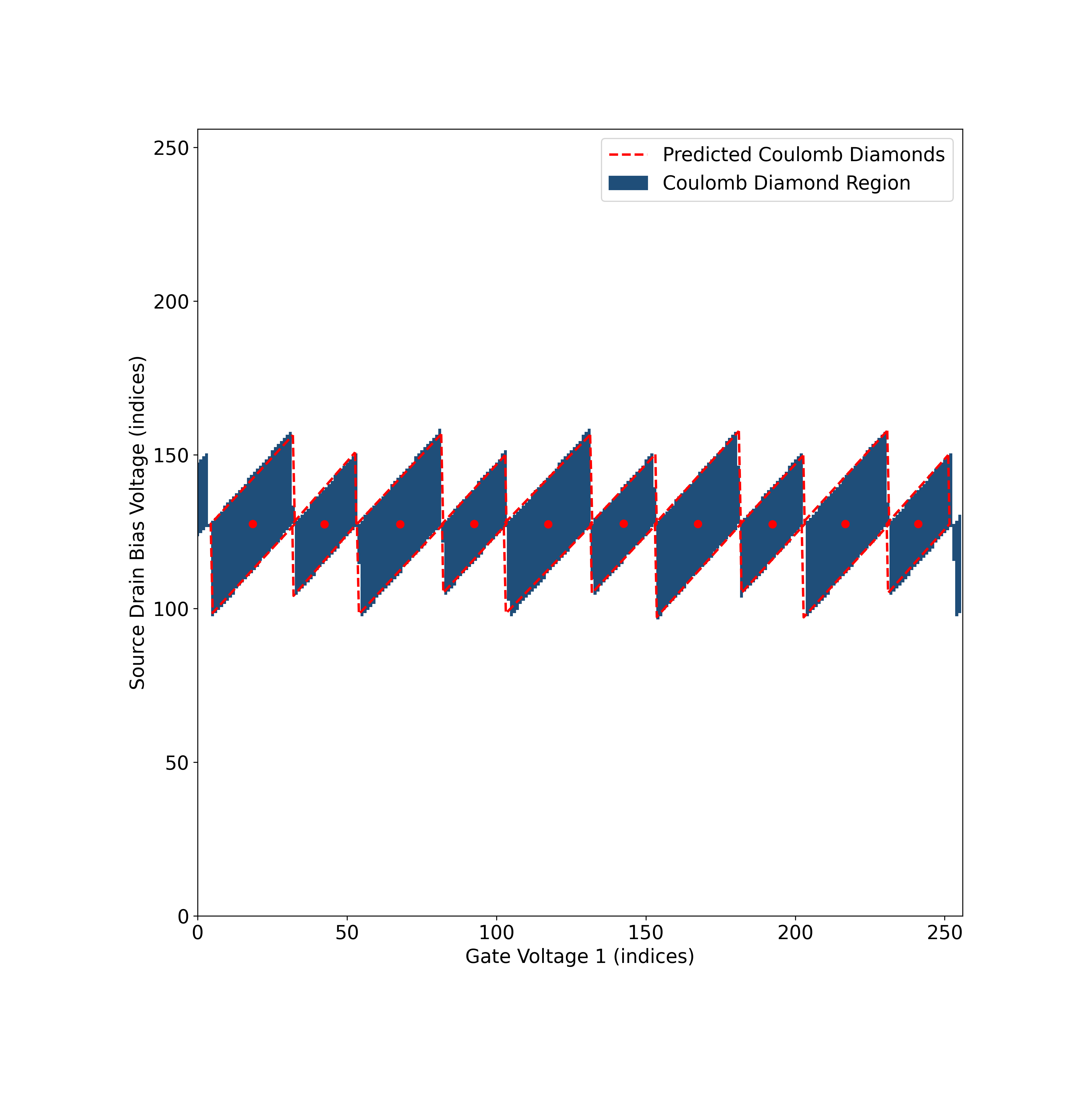
The Coulomb Diamond Detector can detect multiple coulomb diamonds. Download the following example to try it.
Important Notes for Coulomb Diamond Data
- The Coulomb Diamond Segmenter’s inference input can be any arbitrary size
(n, m), but will upscale the image to (256, 256) if it is smaller than 256x256 px. - The Coulomb Diamond Detector’s inference input can be any arbitrary size
(n, m), but will upscale the image to (256, 256) if it is smaller than 256x256 px. - The Coulomb Diamond Segmenter and Detector can be used sequentially to detect coulomb diamond vertices of a 2D conductance grid.
- Diamond vertices outputs will be in pixel coordinates.

